Getting Started with Data Fabric
Data fabric requires rethinking data culture. It shifts the focus from building the data infrastructure to launching data products. Your teams need to make data-driven decisions, but data is siloed and stored in different formats.
Three Pillars of a Successful Data Fabric
Implementing a successful data fabric strategy typically revolves around three key pillars: Integration, Intelligence, and Governance. These pillars provide a framework for building an organization’s cohesive and effective data fabric.
By focusing on the Integration, Intelligence, and Governance pillars, organizations can establish a resilient and effective data fabric that supports their data management and analytics goals. These pillars work together to create a unified and coherent data ecosystem to support your data fabric initiative – enabling organizations to harness the full potential of their data assets.
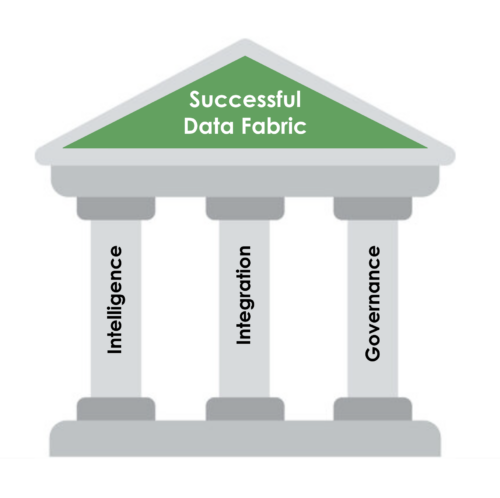
Intelligence
Turning data into actionable insights is crucial for deriving value from a data fabric. This involves leveraging advanced analytics, machine learning, and other intelligent technologies to extract meaningful information from the integrated data. This is achieved by advanced analytics tools, machine learning models for predictive and prescriptive analytics, and advanced business intelligence and data visualization tools.
Integration
Seamless data integration across diverse sources and formats is fundamental to the success of a data fabric. This involves breaking down data silos, connecting disparate systems, and ensuring data flows smoothly across the organization. The key components of Integration are data connectors that enable connection to various data sources, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes for data movement and transformation, and real-time data processing and streaming capabilities.
Governance
Ensuring the quality, security, and compliance of data is a critical aspect of a successful data fabric. Implementing robust data governance practices to maintain data integrity, protecting sensitive information, and adhering to regulatory requirements is key. Implementing tools like data catalog for documentation and discovery, access controls and encryption for data security, and putting compliance monitoring and auditing mechanisms in place.
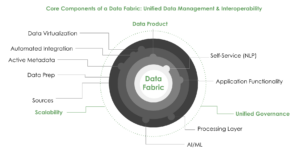
Core Components of Data Fabric
There are many ways to build a data fabric. But for a data fabric to make data easy to find, use, and manage, it should consist of the following core components.
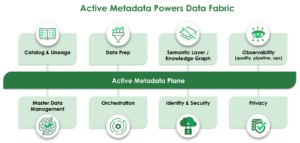
- Active Metadata. The foundation of data fabric is metadata. This includes technical metadata that describes the properties of data sources such as format, data types, and access protocols; business metadata such as labels and classification; social metadata such as tags and annotations; and operational metadata about how data is used.
- Application functionality. The interactive functions of discovery, cataloging, and preparation enable data teams to manage data. They also enable business users to find and work with data.
- Processing layers. The operational work of a data fabric involves providing connections to data sources, managing workflows, abstracting data to create a unified view, and ensuring access to data is appropriately controlled.
- AI/Machine Learning. Using the fabric’s metadata, AI and machine learning automate many aspects of the processing and application functions reducing the workload of data teams and users.
- Data Products. Though data products are not core to data fabric, data fabric provides the foundational framework crucial for constructing data products by addressing key challenges in data management. It offers a unified approach to data access, allowing organizations to seamlessly integrate information from disparate sources, whether on-premises or in the cloud.
Craft a Custom Data Fabric Solution
Explore features aligned with your budget and needs.